Are you wondering if Jamaica is in Africa? It’s a common question and the answer might surprise you. Keep reading to learn more about the Caribbean nation of Jamaica and its location.
Introduction to Jamaica
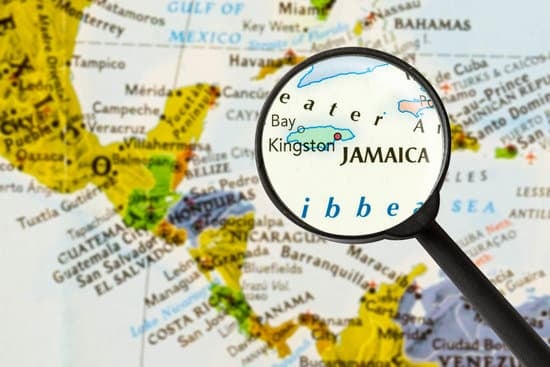
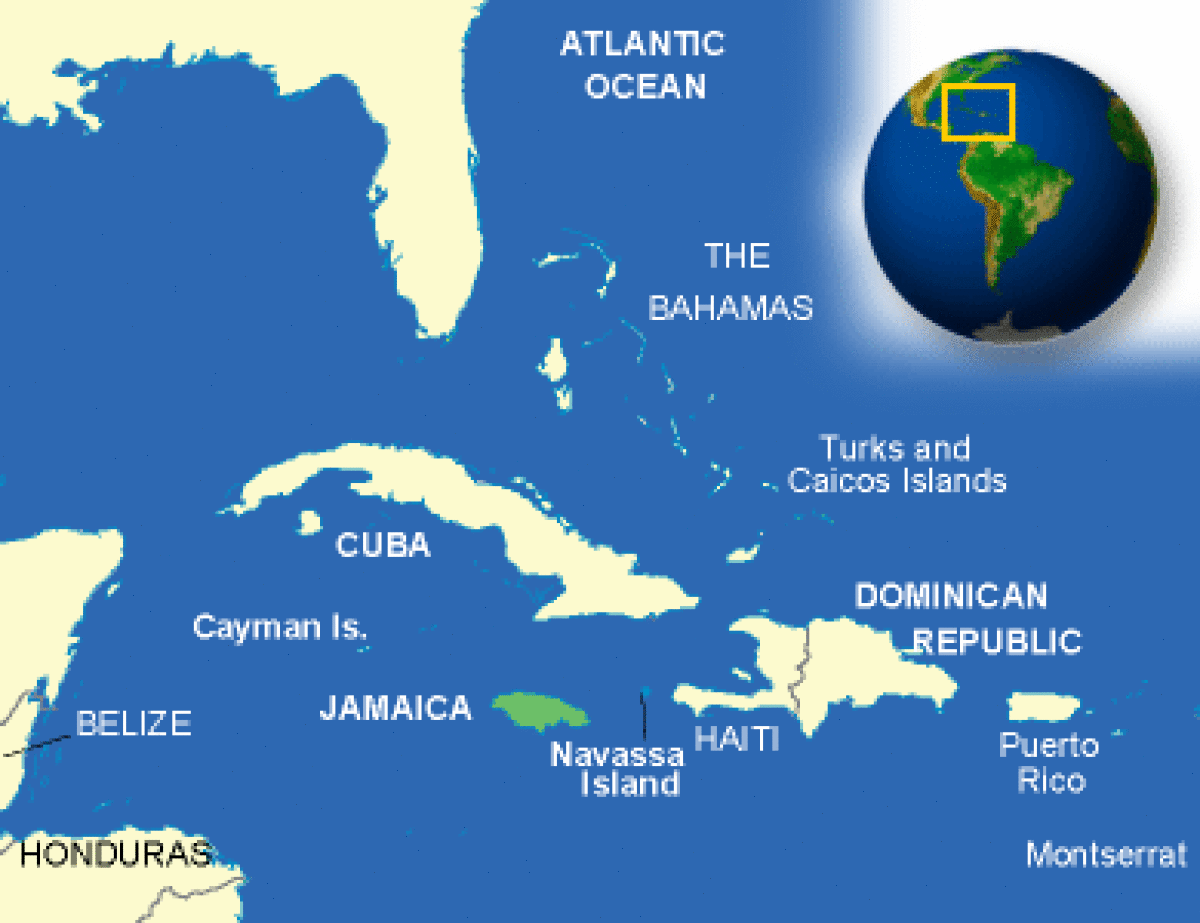
No, Jamaica is not located in Africa. Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea, located 90 miles south of Cuba and 600 miles northwest of Haiti and the Dominican Republic. The majority of Jamaicans are of Sub-Saharan African ancestry, with significant European, Arab, Chinese and Indian influences.

Geographical Location of Jamaica
No, Jamaica is not in Africa. It is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea, about 145 kilometers (90 miles) south of Cuba and 161 kilometers (100 miles) southwest of Haiti.
Is Jamaica Part of Africa?
No, Jamaica is not part of Africa. Jamaica is an island country located in the Caribbean Sea, north of South America. The majority of Jamaicans are of Sub-Saharan African ancestry, with significant European, East Asian and Indigenous American influences. Most Jamaican slaves came from the region of modern day Ghana, Nigeria and Central Africa, and included the Akan, Ashanti, Yoruba, Ibo and Ibibio peoples.

History of the African Diaspora in Jamaica
No, Jamaica is not located in Africa. Jamaica is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and west of Haiti. The African diaspora in Jamaica began when the first Africans were brought to the island by the Spanish in 1513. These Africans were taken from their homes in West Africa and transported to Jamaica as slaves to work on plantations owned by Europeans. Over time, these African slaves and their descendants developed a unique culture that blended elements of their African heritage with those of the Caribbean and European cultures they encountered.

Cultural Influences from Africa in Jamaica
No, Jamaica is not located in Africa. However, the culture of Jamaica has been heavily influenced by African culture due to the large number of African slaves that were brought to the island during colonial times. This influence is seen in Jamaican music, food, language, and religion. African derived customs such as yabbah pottery and Akan cultural influences are also evident in Jamaican culture.

The Language Spoken in Jamaica
No, the language spoken in Jamaica is not Jamaican in Africa. The official language of Jamaica is English, but the majority of the population speaks Jamaican Patois, an English-based creole language with West African influences.
Music and Dance Influences from Africa in Jamaica
No, Jamaica is not in Africa. Jamaica is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and northwest of Haiti. However, Jamaica has a strong African influence due to its history of slavery and colonization. African music and dance have been deeply embedded into the culture of Jamaica, with many traditional dances such as Bruckins being a fusion of African and British influences. The one-drop rhythm, which is the defining rhythmic element of reggae music, is distinctly African. The call-and-response style of singing which is so common in Jamaican music also has its roots in African music. Additionally, many aspects of Jamaican culture such as language, cuisine, proverbs and drumming have been influenced by Africa.
Cuisine and Food Influences from Africa in Jamaican Culture
No, Jamaica is not located in Africa. Jamaica is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and west of Haiti. However, African culture has had a significant influence on Jamaican culture, including its cuisine. The importation of enslaved people from West Africa brought with it many culinary traditions, such as jerk sauce. Jamaican cuisine also includes a mixture of cooking techniques, flavours and spices influenced by Amerindian, African, Irish, English, French and Spanish cultures. Today, jerk pork, jerk chicken and jerk fish are popular dishes that reflect the influence of African cuisine in Jamaican culture.
The Religious Beliefs of Jamaicans with African Roots
No, Jamaica is not located in Africa. It is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and west of Haiti. While Jamaica’s Christian roots hail from Europe, several other forms of Christianity are also practiced locally that are strongly marked by African influences. Jamaican religious traditions in the United States include Obeah, Jamaican Revivalism or Pukumina, and Rastafari. Obeah is a system of herbal and spiritual healing that has its roots in West African religious practices. The Rastafarian movement is based on the belief that Haile Selassie was God and the Black Messiah, and their faith is organized around this belief. The Kumina community also has strong African roots and their sense of ethnic affiliation and identity is closely linked to their African heritage.

Education and Social Mobility among Jamaicans with African Descent
No, Jamaica is not located in Africa. Jamaica is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and west of Haiti. Although the majority of Jamaicans are of African descent, the country is not part of Africa. Education and social mobility among Jamaicans with African descent has been a long-standing issue in Jamaica due to the traditional ranking of white, colored, and black. Historically, education was seen as one of the key ways to gain upward social mobility and acceptance for those with African ancestry in Jamaica. With more than 90 percent of the population identifying as Black, Jamaica’s inequality has long been seen as class- rather than race-based.

Contemporary Issues Affecting the African Community in Jamaica
No, Jamaica is not in Africa. Jamaica is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and west of Haiti. The African community in Jamaica has been affected by a number of contemporary issues, including migration and crime, psychological problems stemming from the legacy of slavery, and conflicts over the place of Africa in Jamaica’s past and present. Additionally, the policy of centering hybridity has effectively marginalized the country’s majority black population. To address these issues, there is a need for an in-depth understanding of Jamaican history and culture to inform policies that promote social cohesion and justice.

Popular Attractions for Tourists Visiting African Communities in Jamaica
No, Jamaica is not in Africa. Jamaica is an island country located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and west of Haiti. Popular attractions for tourists visiting African communities in Jamaica include the Bob Marley Museum, Trench Culture Yard Museum, Dunn’s River Falls and Park, Mystic Mountain near Ocho Rios, golfing, beaching, hiking, dancing, ghostbusting and cave-diving. Other popular attractions include Reach Falls on the White River and Montego Bay.

How Can People Help Support the African Communities In Jamaica?
People can help support the African communities in Jamaica by providing different types of assistance such as food, clothing, and medical supplies. Additionally, people can support the African communities in Jamaica by donating to organizations that are dedicated to preserving and promoting the culture and heritage of Jamaica’s African roots. Finally, people can also help by visiting or volunteering at museums and other cultural institutions that are dedicated to preserving the history of Jamaica’s African heritage. No, Jamaica is not located in Africa; it is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea.
Conclusion
No, Jamaica is not in Africa. Jamaica is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and west of Haiti. It has a long history of colonization by the Spanish, British, and French, and its population is largely descended from African slaves brought to the island by European colonists.