If you’re curious about what continent is Jamaica in, look no further! Jamaica is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea and is part of the continent of North America. Here, we’ll explore some interesting facts about Jamaica and its geography.
Introduction
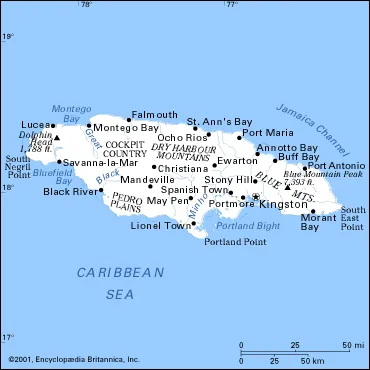
Jamaica is an island country located in the Caribbean Sea, approximately 90 miles south of Cuba. It is the third largest island in the Caribbean Sea and has a population of 2.8 million people. Jamaica has a rich history that dates back to when the original inhabitants – the Arawaks (also known as Tainos) – came from South America over 2,500 years ago. The country is part of North America and its culture has been influenced by a variety of cultures, including English, African, Indian and Chinese. Jamaica boasts a unique landscape with lush rainforests filled with exotic plants and animals, stunning beaches and vibrant cities full of music and culture. With its warm climate, friendly people and numerous attractions, Jamaica has become one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world!
Overview of Jamaica
Jamaica is a beautiful island nation located in the Caribbean Sea. With its stunning beaches, lush green mountains, and vibrant culture, Jamaica is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world. It is home to nearly 3 million people who speak English as their primary language.
Jamaica’s geography consists of 11,000 square kilometers (4,247 sq mi) of mountainous terrain and coastal plains. Its climate is tropical with hot and humid summers as well as mild winters. The country has two rainy seasons from May to October and from November to April.
The culture of Jamaica has been influenced by African, European, and Asian cultures throughout its history. Music plays an important role in the culture with genres such as reggae, ska, mento, calypso and rocksteady being particularly popular. There are also many festivals that take place throughout the year celebrating Jamaican culture including Jamaica Jazz & Blues Festival which takes place at Montego Bay every January.
Jamaica has a rich history that dates back to when it was inhabited by Arawak Indians before being colonized by Spain in 1494 followed by Britain in 1655. The country gained independence in 1962 with Queen Elizabeth II still being recognized as its head of state today through her representative Governor-General Patrick Allen who resides at King’s House in Kingston which serves as the official residence for all governors-general since it was built in 1762 during British rule.
Jamaica offers visitors many attractions including Dunn’s River Falls near Ocho Rios which can be seen cascading down 600 feet into the Caribbean Sea below; Blue Lagoon located near Port Antonio where visitors can go swimming or snorkeling
Geography of Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea, about 600 miles (965 kilometers) south of Miami. Spanning 10,990 square kilometres (4,240 sq mi) in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the fourth-largest island country in the Caribbean. Jamaica is bordered by Haiti to its west and Cuba to its north. The Queen is represented in Jamaica by the Governor-General.
Jamaica is a mountainous island with lush tropical rainforests and beautiful blue waters along its coastlines. The highest point on the island is Blue Mountain Peak at 7,402 feet (2256 m). There are numerous rivers on Jamaica including Rio Cobre which flows through Spanish Town and Stony Hill River which runs right into Kingston Harbor.
The tropical climate of Jamaica allows for an abundance of plant life on the island making it well known for its breathtaking landscapes. The economy of Jamaica heavily relies on tourism from visitors coming to experience its stunning beaches and beautiful landscapes as well as activities such as snorkeling and diving that can be done around its coasts.
Jamaica also has a wide variety of wildlife both native to the region such as parrots, hummingbirds, iguanas, bats and lizards as well as introduced species such as goats, donkeys and horses brought over by settlers hundreds of years ago.
What Continent Is Jamaica In?
Jamaica is an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, which is part of the Greater Antilles chain of islands. The country lies almost exactly between North and South America and is the third-largest English-speaking country in the Americas, after the United States and Canada. Jamaica has a rich culture and history, with its diverse population reflecting influences from both Africa and Europe.
The island nation is considered a part of North America, even though it lies geographically in the Caribbean region. Jamaica has long had strong ties to both North America and Central America, as well as to Europe. This connection to other regions gives Jamaica an incredibly varied culture that can be seen in its food, music, art and language.
Jamaica has been a member of the Commonwealth since 1962 when it gained independence from Great Britain. It is also a member of many international organizations such as CARICOM (Caribbean Community), OAS (Organization of American States) and ALBA (Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our Americas). Jamaica’s economy relies heavily on tourism but it also exports bauxite ore, sugar cane products, bananas and apparel items.
In addition to its cultural ties with other countries around the world, Jamaica maintains close political ties with other countries in its region such as Cuba, Haiti and Trinidad & Tobago. The country’s location makes it ideally placed for trade between these countries as well as North American nations like Canada or Mexico.
Jamaica’s unique culture makes it one of a kind on this continent; no other Caribbean island offers this combination of African heritage blended with European customs – making it truly one-of-a-kind!
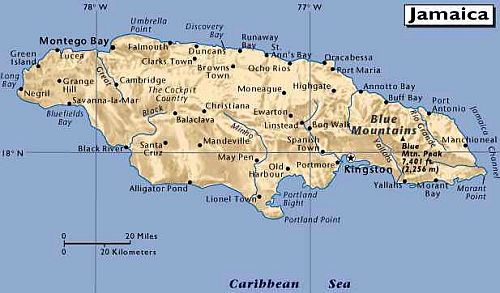
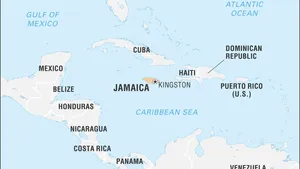
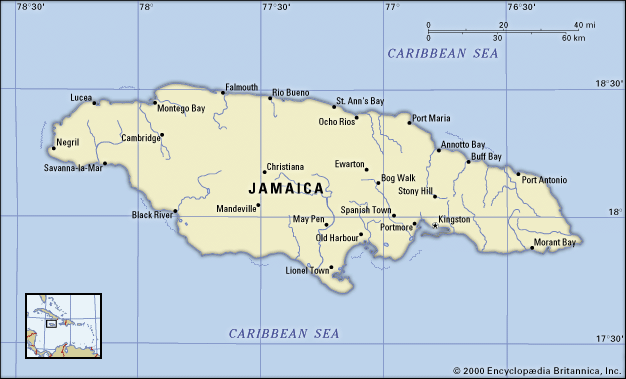
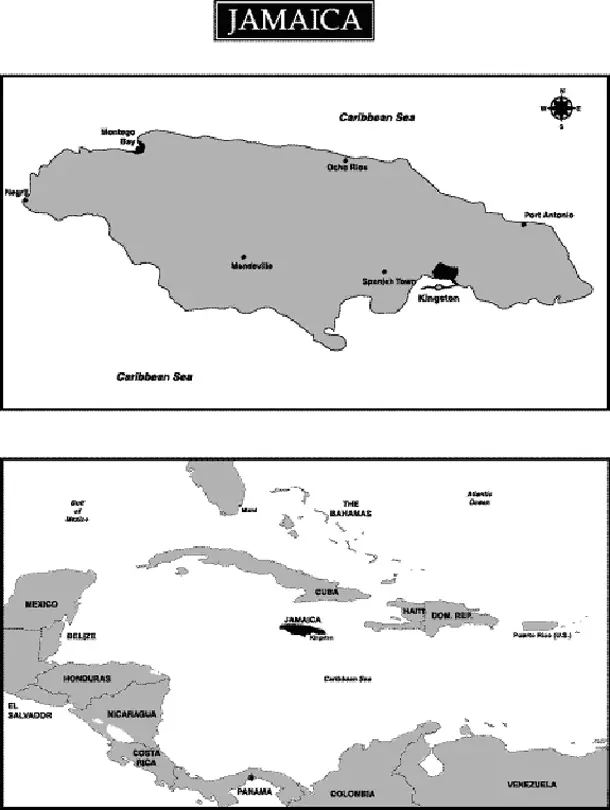
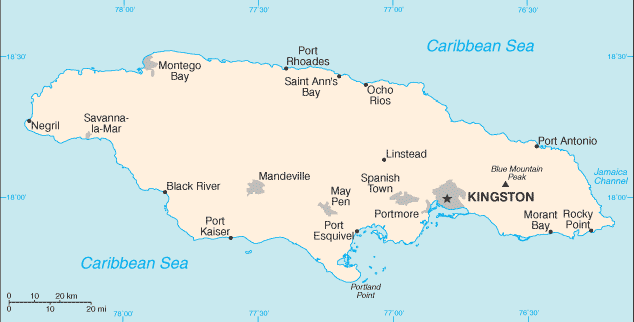
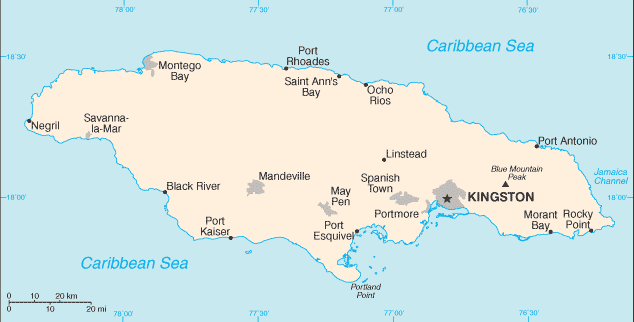
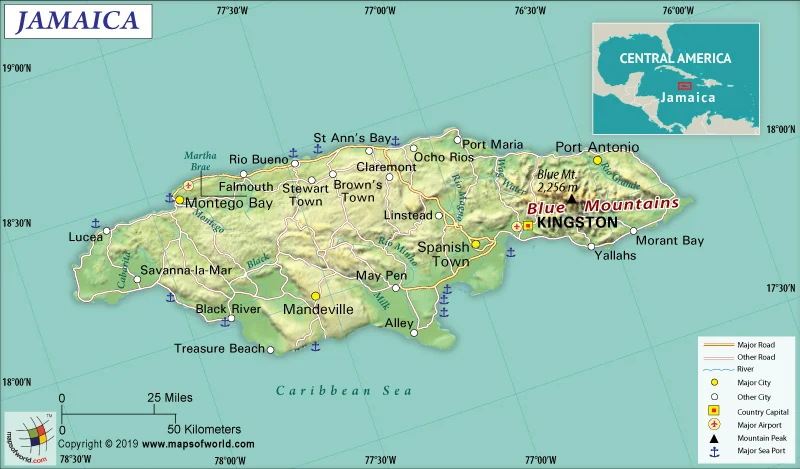
Where is Jamaica on the map
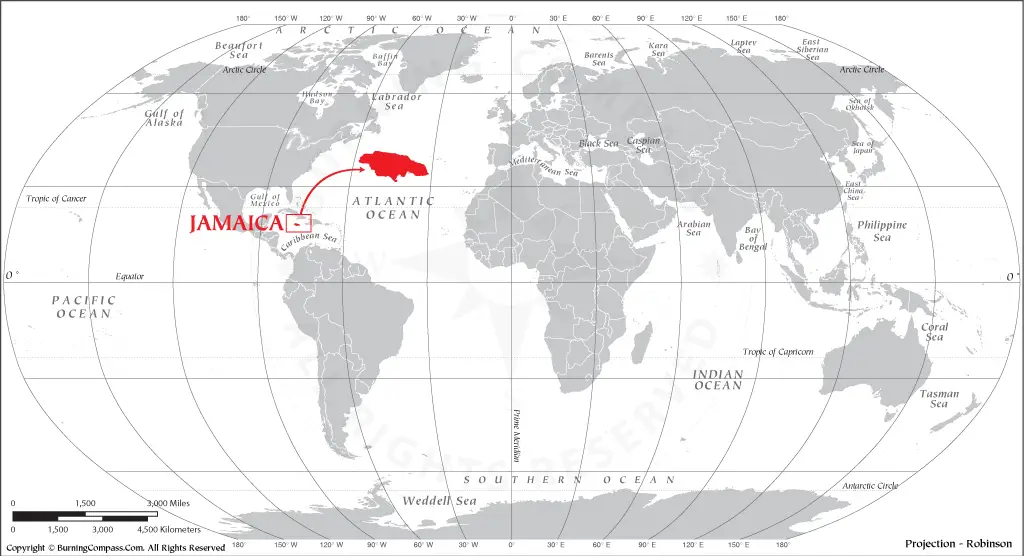
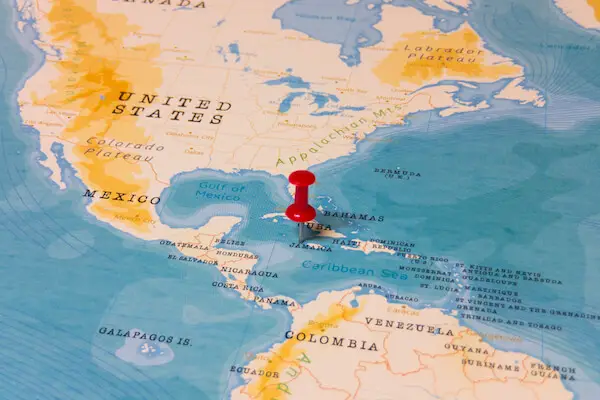
Jamaica is an island country located in the Caribbean Sea. It is situated south of Cuba and west of Hispaniola, the island containing Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Jamaica’s capital city is Kingston, located on the southeastern coast. The island covers a total area of 10,990 square kilometers (4,240 square miles) and has a population of over 2.9 million people.
The geography of Jamaica is diverse, featuring lush rainforests in its interior and white sand beaches along its coasts. The Blue Mountains rise to over 2,200 meters (7,000 feet) above sea level in the eastern part of the island and provide stunning views for visitors to enjoy.
Jamaica can be easily discovered on a map as it lies at latitude 17°30’ north and longitude 76°50’ west. It is also one of the Greater Antilles islands which form an arc from Cuba in the north to Trinidad and Tobago in the south. Other well-known islands nearby include Hispaniola (Haiti/Dominican Republic), Puerto Rico, Hispaniola (Cuba), Cayman Islands, Turks & Caicos Islands among others.
The rich culture of Jamaica has been influenced by its history including Spanish colonial rule followed by British colonization until 1962 when it gained independence as a Commonwealth realm with Queen Elizabeth II as head of state. Today Jamaicans are known for their warm hospitality towards visitors to their shores as well as their love for music such as Reggae which originated here!
Climate in Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. It boasts a tropical climate, where temperatures rarely dip below 32 degrees Celsius and the average high temperature reaches around 35 degrees Celsius. The northeast trade winds are dominant throughout the year and bring with them cooling breezes that can help combat the heat. Two distinct climates are found in Jamaica – an upland tropical climate on the windward side of the mountains and a semi-arid climate on the leeward side. Cold fronts from North America arrive from mid-October to mid-April, bringing with them short periods of cooler weather. When it comes to precipitation, Jamaica experiences both heavy rainfall during its wet season (May through October) and dry conditions during its dry season (December through April). Additionally, Jamaica is home to diverse flora and fauna, vibrant marine life, and some pollution issues in certain areas. With its beautiful beaches, lush rainforests, and stunning mountain landscapes, Jamaica offers plenty for nature lovers to enjoy!
Biodiversity in Jamaica
Jamaica is a beautiful Caribbean island that is home to a diverse range of wildlife. With its lush rainforests, coral reefs and mangrove swamps, the country offers an abundance of biodiversity, making it an important asset to the planet. From unique species of birds and animals, to vibrant plant life, Jamaica is a natural paradise which must be protected and conserved.
The Blue and John Crow Mountains National Park was established in 1992 in order to protect Jamaica’s biodiversity. This park provides refuge for many different kinds of birds such as the endemic Jamaican Blackbird and the Orangequit. It also protects endangered mammals including the Jamaican Hutia, which is one of only two species native to Jamaica.
Jamaica has over 3,304 vascular plant species, with 600 ferns varieties and 136 species of orchids found on the island. The country also boasts over 3500 species of mollusks including snails, slugs and squids. In addition, there are numerous seagrass beds around the coastlines providing habitats for a variety of sea creatures such as turtles and fish.
Jamaica’s biodiversity is under threat due to deforestation caused by urban growth as well as unsustainable agricultural practices such as burning fields which can cause soil erosion and water pollution – both serious issues which need urgent attention if they are to be tackled effectively. Conservation efforts are necessary if we are going to preserve this precious environment for future generations.
People and Culture of Jamaica

Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea, and is known for its rich culture, diverse population, and vibrant atmosphere. The original inhabitants of Jamaica are believed to be the Arawaks, also called Tainos. They arrived from South America 2,500 years ago and were later joined by other ethnicities including East Indians, Africans, Chinese and Europeans. As a result of this mix of cultures, Jamaican culture today is a unique blend of many different influences.
Jamaican Creole (also known as Patois) is the main language spoken in Jamaica and is a mix of English words with African dialects. This colorful language has become an important part of Jamaican culture as it helps to unite all people regardless of their background or class. Additionally, there are many other cultural influences seen in Jamaican music such as Reggae, Ska, Mento and Dancehall which draw upon elements from many different sources including African rhythms, European melodies and even Indian instruments.
Jamaica’s national identity is closely intertwined with its religion; Christianity remains the predominant faith with around two-thirds of the population being members of various denominations such as Roman Catholicism or Anglicanism. Other religions practiced on the island include Hinduism, Islam and Rastafari which have each made their own contributions to Jamaican culture over time.
In addition to its religious components, Jamaica’s national identity is also defined by its class structure; most Jamaicans are either working class or middle class with only a tiny percentage belonging to the upper class elite who control most aspects of society from politics to economics. Despite these disparities however all Jamaicans share an appreciation for life’s
What Language is Spoken in Jamaica
Jamaica is a Caribbean island known for its beautiful beaches, delicious cuisine, and vibrant culture. While English is the official language of Jamaica, the most widely spoken language is Jamaican Patois. Jamaican Patois, or Patwa, is an English-based creole language with West African influences. It has formed its own unique culture in Jamaica and has been a source of pride for many generations of Jamaicans.
Jamaican Patois has become increasingly popular due to the success of reggae music and other genres that incorporate it into their lyrics. It has also been used in popular films such as Cool Runnings and The Harder They Come. Although English remains the primary language used in government, media, religious, and educational institutions in Jamaica, Jamaican Patois is becoming more prevalent among everyday conversations and interactions.
The British Empire colonized Jamaica during pre-columbian times which led to the introduction of British English as the official language of Jamaica. This influenced how Jamaicans spoke English which then evolved into its own dialect over time known as “Jamaican” or “Creole” today.
The dialect spoken by Jamaicans varies depending on where you are on the island but all share similarities with one another such as slang words like “brawta” meaning “anything good or extra” or “yuh suh di ting deh” meaning “you are doing that thing right there”. Additionally, some words have multiple meanings depending on context such as the word “dutty” which can mean either dirty or mean/rude depending on how it’s used within a sentence.
Overall, while
Religion in Jamaica
Jamaica is an island in the Caribbean Sea known for its vibrant culture and religious diversity. The largest religion practiced in Jamaica is Protestantism, making up 65% of the population. This includes denominations such as the Church of God, Seventh-day Adventist, and Pentecostal churches. Other religious beliefs found on the island include the African-influenced Rastafari religion, Hinduism, Catholicism, and traditional African religions.
The Rastafari religion was born in Jamaica in the early 1930s and has since spread around the world. It is rooted in African spirituality, with a focus on liberation from oppression and repatriation to Africa. Many adherents believe that Haile Selassie I, Ethiopia’s last emperor is a divine figure who will lead them back to their homeland.
Hinduism has been present on the island since 1845 when Indian immigrants arrived to work as indentured laborers. They brought with them their own beliefs and practices which have been adapted over time to fit into Jamaican culture.
Catholicism was introduced by Spanish settlers during colonial times but today only makes up a small percentage of believers in Jamaica (about 5%). Traditional African religions are also still practiced by some people who hold ancestral spirits and deities sacred while also incorporating elements of Christianity into their worship practices.
Overall, Jamaica is an incredibly diverse country with many different belief systems being practiced side by side in harmony. Despite having different faiths, Jamaicans celebrate each other’s holidays and work together to create a strong sense of unity within the nation.
Government and Politics of Jamaica
Jamaica is an independent country located in the Caribbean Sea. It has a rich history and culture, as well as a unique form of government and politics. Jamaica is a constitutional monarchy with two legislative houses – the House of Representatives and the Senate. Head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who is represented by the Governor-General.
The 1962 Constitution of Jamaica established parliamentary democracy based on a system of representative and responsible government. The executive branch consists of the Prime Minister, who is appointed by the Governor General on advice from Parliament, as well as other ministers. The legislative branch is bicameral with members from both chambers elected by popular vote for five-year terms.
Jamaica has seen some changes in its political landscape over time, including independence from Britain in 1962, increasing tourism industry impact and rebuffing calls for reparations to Jamaica for slavery. Nationalism has also been a major factor in Jamaican politics as citizens strive for self-government, social justice, economic justice and national identity.
Education System in Jamaica
Education in Jamaica is based on the British system, with six years of primary school education being compulsory and free for all. Private primary schools provide quality education that is on par with similar schooling in other countries. Since the emancipation of slaves in 1834, educational, health and social services have greatly improved. A savings back system has also been established island-wide.
Jamaica is an island country located in the Caribbean Sea and is represented by a Governor-General appointed by the Queen. It covers 11,000 square kilometers and consists of numerous roads, bridges and railways that allow students to travel between schools easily.
With a good infrastructure in place, Jamaica’s educational system has been able to provide quality education to its citizens over the years. Primary school focuses on providing students with basic knowledge such as reading, writing and arithmetic while secondary school prepares them for higher studies or vocational training programs. Higher education options include universities and technical institutes which offer various courses related to business administration, engineering or other fields of study. With proper guidance from parents and teachers alike, students can aspire to become successful professionals after their studies are complete.
Health Care System in Jamaican
Jamaica has a fragmented system of health care which is currently undergoing a transformation. The goal is to provide efficient, person-centered care that meets the needs of all Jamaicans.
Universal access to primary health care and education up to the secondary level is being made available through the Programme for Advancement through Health and Education (PATH). PATH provides financial assistance for medical treatment and other basic needs, as well as offering support services such as counseling and job training.
Jamaican root tonics are traditional fermented beverages made with ingredients such as roots, bark, vines, and dried leaves. These local remedies are used to treat various ailments in Jamaica and are an important part of their culture.
The Jamaican government has taken steps to improve their health care system by investing in technology and modernizing equipment at hospitals. This includes installing electronic medical records systems, providing access to telemedicine services, and improving the quality of healthcare personnel training. They are also focused on addressing social determinants of health such as poverty, inadequate housing or nutrition, lack of education or employment opportunities, violence or social exclusion.
Overall Jamaica’s health care system is making strides towards providing quality healthcare for its citizens but there is still much work that needs to be done in order to ensure adequate access for everyone.
Tourism Industry in Jamaican
Jamaica is an upper-middle income country with a vibrant tourism industry. Every year, over 4.3 million tourists flock to the island nation to experience its unique culture, stunning natural beauty, and world-class resorts. The country’s economy is heavily reliant on tourism, which accounts for around 10% of its gross domestic product.
The leading countries of origin for international overnight visitors in Jamaica include the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. Tourists can stay at a range of accommodation options including world-famous all-inclusive resorts and upscale hotels and villas in six resort destination areas: Montego Bay (9,307 rooms), Ocho Rios (8,202 rooms), Negril (7,574 rooms), Port Antonio (2,205 rooms), Runaway Bay (1,819 rooms) or South Coast (1,686 rooms).
Jamaica’s transformation of its tourism sector has been driven by investments from companies such as Spanish hotel chain Riu Palace Jamaica who opened their flagship hotel in Montego Bay in 2018. This influx of new investment has helped to create thousands of jobs providing employment opportunities across the island while also increasing visitor numbers and revenue for the local economy.
As well as offering a wealth of accommodation options and entertainment activities such as golf courses and beaches to explore; Jamaica is renowned for its unique culture which includes reggae music and dancehall vibes. It is also home to some incredible historical sites such as Seville Great House & Heritage Park – one of the oldest plantations still standing in Jamaica today – providing an interesting insight into the country’s past that visitors can enjoy during their stay on the island.
–Conclusion
Conclusion is the last part of something such as an essay, speech, or argument. It is used to summarize the main points and restate the thesis or main idea of the piece. The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader and make them think about the topic further. It should also provide closure to any unanswered questions or arguments that were presented throughout the body of work.
